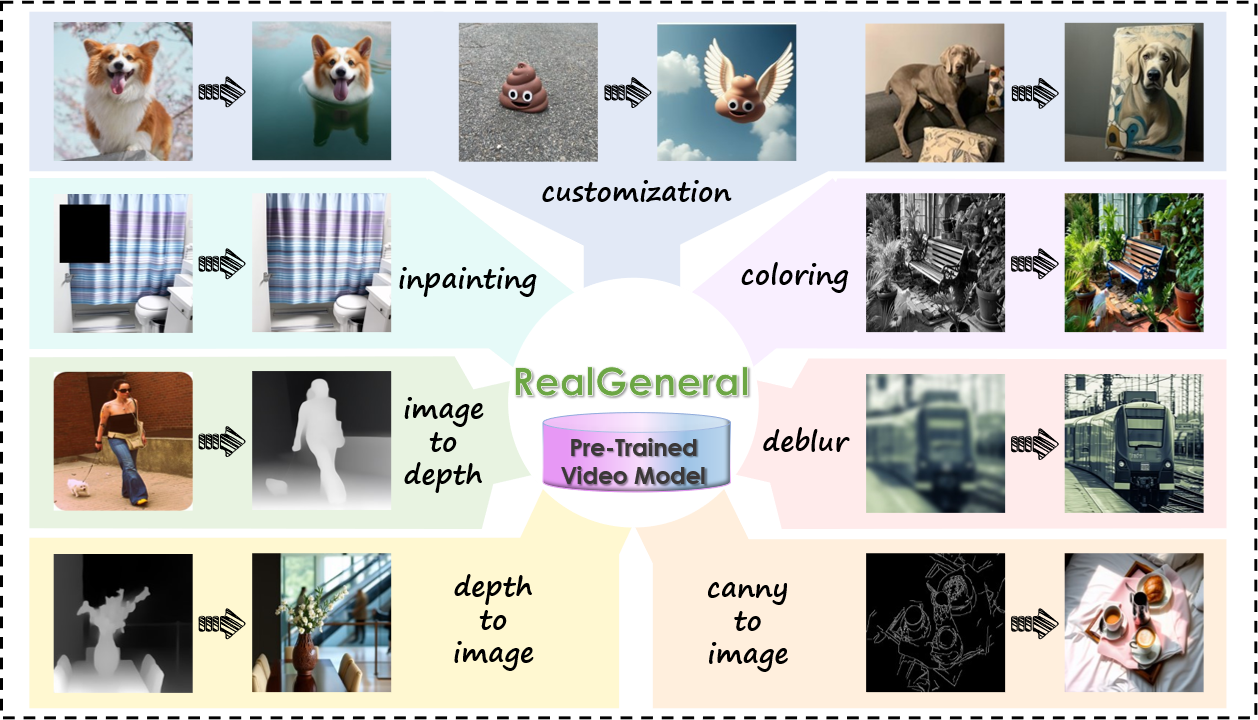
Unifying diverse image generation tasks within a single framework remains a fundamental challenge in visual generation. While large language models (LLMs) achieve unification through task-agnostic data and generation, existing visual generation models fail to meet these principles. Current approaches either rely on per-task datasets and large-scale training or adapt pre-trained image models with task-specific modifications, limiting their generalizability. In this work, we explore video models as a foundation for unified image generation, leveraging their inherent ability to model temporal correlations. We introduce RealGeneral, a novel framework that reformulates image generation as a conditional frame prediction task, analogous to in-context learning in LLMs. To bridge the gap between video models and condition-image pairs, we propose (1) a Unified Conditional Embedding module for multi-modal alignment and (2) a Unified Stream DiT Block with decoupled adaptive LayerNorm and attention mask to mitigate cross-modal interference. RealGeneral demonstrates effectiveness in multiple important visual generation tasks, e.g., it achieves a 14.5% improvement in subject similarity for customized generation and a 10% enhancement in image quality for canny-to-image task.
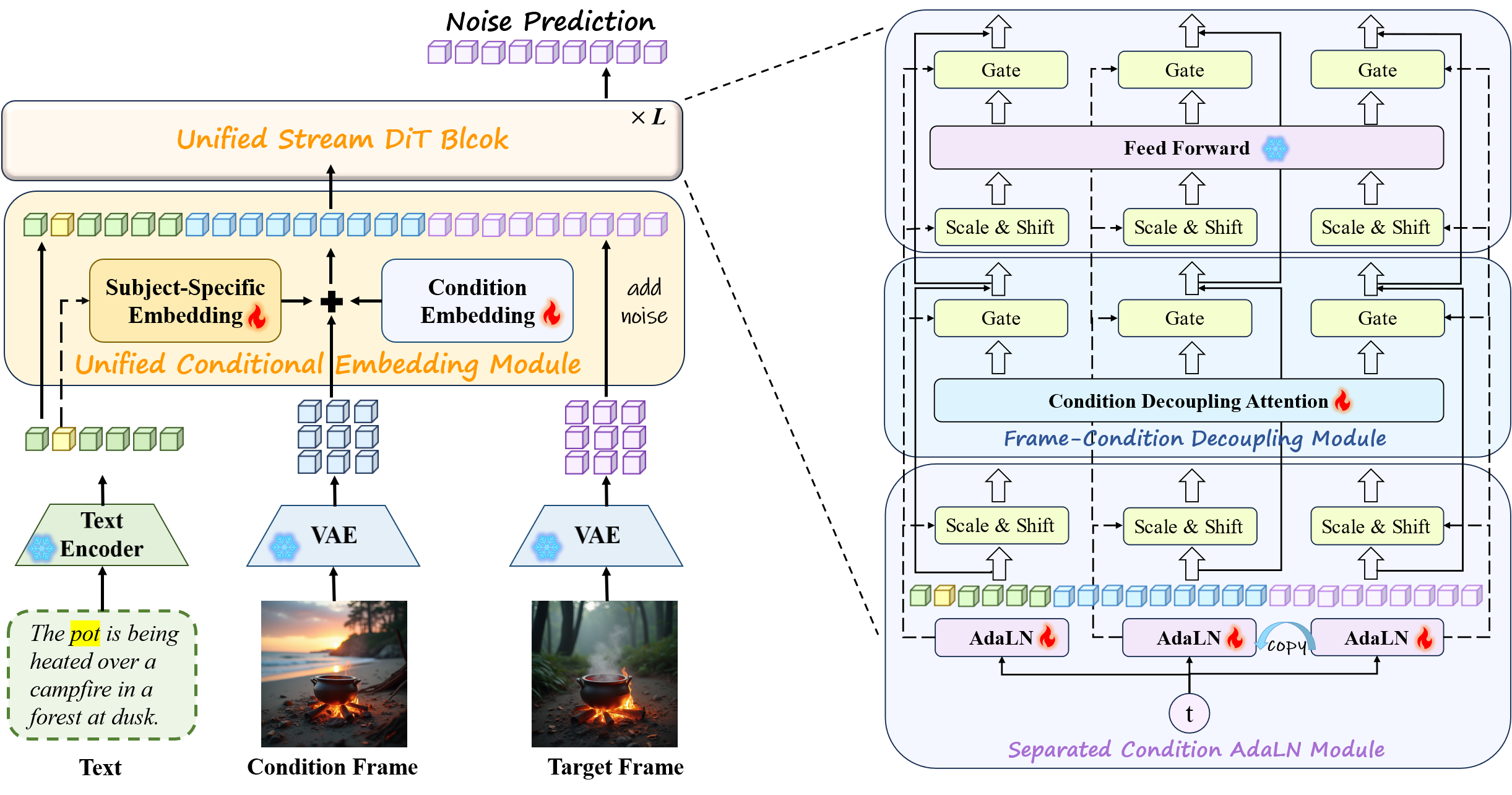
Core Idea:
Inspired by LLMs that unify textual generation through unlabeled large-scale text pretraining and in-context learning abilities,
we argue that the video foundation model pre-trained on massive continuous visual data can similarly unify the visual generation tasks.
Analogous to how LLMs autoregressively predict tokens conditioned on previous context, video models can naturally extend this concept to
temporal visual frames, predicting subsequent frames from preceding ones. We show two frames here for simplicity.
Training Paradigm:
First, two images are separately encoded by VAE. The Unified Condition Embedding Module integrates textual and global task priors into
the condition frame while adding noise to the target frame. Then all tokens are concatenated into a sequence entering the Unified Stream
DiT Block. The Separated Condition AdaLN Module modulates text, condition, and target tokens independently via three distinct branches,
enforcing semantic separation between condition and target frame.
The Frame-Condition Decoupling Module employs an attention mask to prevent interactions between the condition image and text.
We train RealGeneral using LoRA.
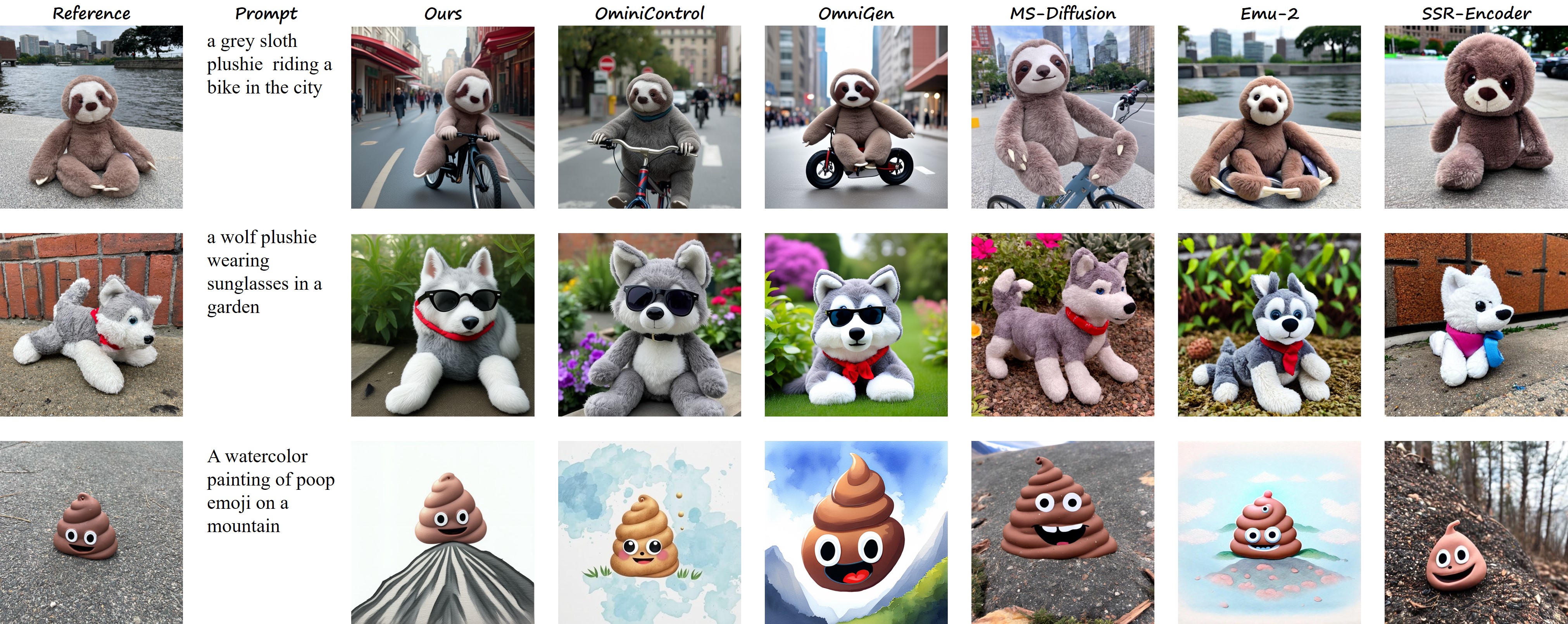

Qualitative results: Compared to other methods, RealGeneral produces more precise details and better adherence to the prompt, underlining its effectiveness in both subject consistency and text controllability for multiple tasks.
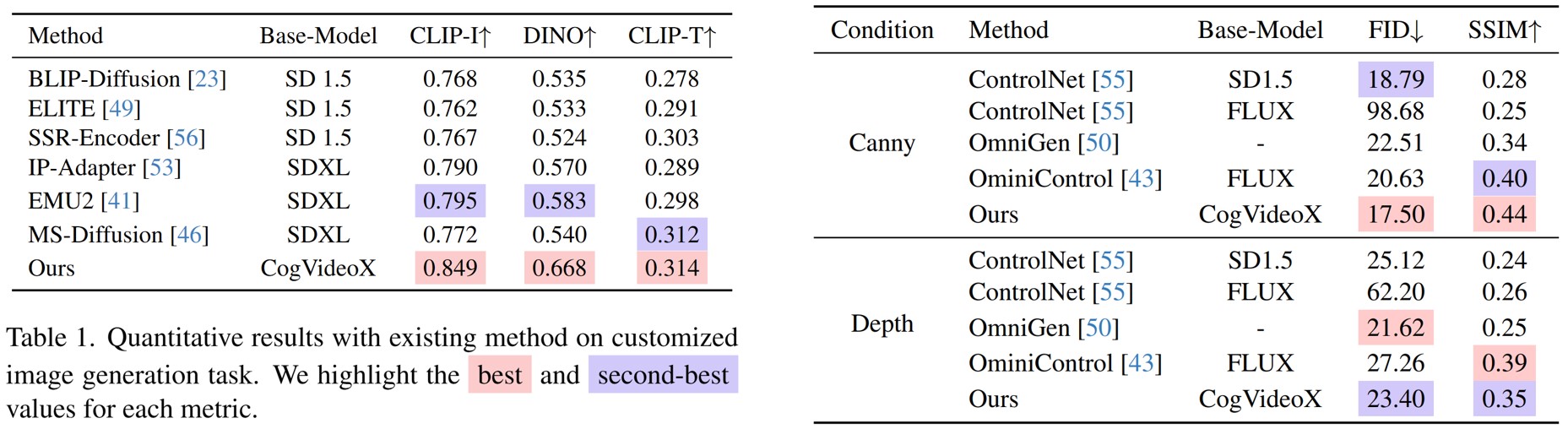
Quantitative results: Compared to existing methods, our method demonstrates significant improvement in image similarity, while attains comparable CLIP-T score.




